RTC Usage
1. RTC Introduction
RTC: (Real-Time Clock)
HYM8563 is a low-power real-time clock (RTC) chip used to provide accurate time and date information. It provides a programmable clock output, an interrupt output, and a power-fail detector. All addresses and data are serially transmitted via the I2C bus interface. The maximum bus speed is 400Kbits/s, and the embedded address register will automatically increment after each read or write operation.
The following are the main features and functions of the HYM8563 chip:
- Clock and Calendar Functions: HYM8563 has clock and calendar functions, providing accurate time and date information. It supports the display and timing of years, months, days, weeks, hours, minutes, and seconds.
- Battery Power Supply: To maintain the persistence of time and date, the HYM8563 chip has a built-in battery power supply circuit, allowing it to continue running even when the main power is disconnected.
- Alarm Function: The chip integrates an alarm function, allowing users to set the alarm time and trigger an alarm when the specified time is reached.
- Timer Function: The HYM8563 chip also has a timer function, enabling users to set the start time and duration of the timer, and triggering corresponding events when the timer expires.
- Temperature Compensation: The chip has a temperature compensation function, which can automatically adjust the clock frequency according to the ambient temperature to maintain accurate timekeeping.
- Communication Interface: HYM8563 communicates with the main controller chip or microprocessor through the I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) interface. This interface is simple and widely used in many embedded systems.
2. HYM8563 Clock Debugging
2.1 Schematic
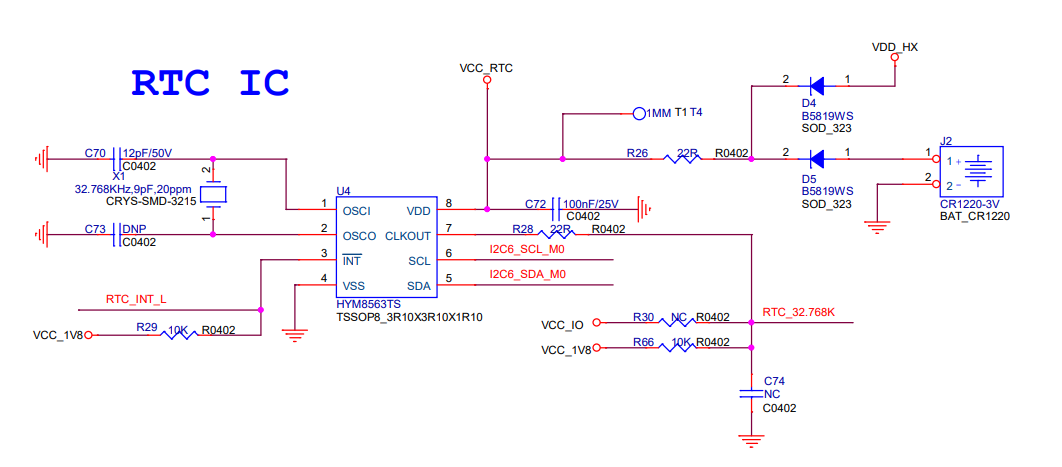
2.2 Driver
- kernel/drivers/rtc/rtc-hym8563.c
2.3 Kernel Configuration
- rockchip_linux_defconfig configuration:
CONFIG_RTC_HCTOSYS=y # Allow RTC time to be set to system time
CONFIG_RTC_HCTOSYS_DEVICE="rtc0" # Default RTC device for time synchronization
CONFIG_RTC_SYSTOHC=y # Allow system time to be set to RTC
CONFIG_RTC_SYSTOHC_DEVICE="rtc0" # Default RTC device for time synchronization
2.4 Device Tree Node Configuration
&i2c6 {
status = "okay";
hym8563: hym8563@51 {
compatible = "haoyu,hym8563";
reg = <0x51>;
#clock-cells = <0>;
clock-frequency = <32768>;
clock-output-names = "hym8563";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&rtc_int>;
interrupt-parent = <&gpio0>;
interrupts = <RK_PB0 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_LOW>;
};
};
&pinctrl {
hym8563 {
rtc_int: rtc-int {
rockchip,pins = <0 RK_PB0 RK_FUNC_GPIO &pcfg_pull_none>;
};
};
};
2.5 Debugging
- Check if the RTC is mounted on the I2C bus:
sudo i2cdetect -y 6
armsom@armsom:~$ sudo i2cdetect -y 6
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- 51 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
We can see that an I2C device (RTC) with an address of 0x51 is mounted on the I2C bus /dev/i2c-6.
3. RTC Testing
The Linux system includes two times: system time and RTC time.
Commands like date and time in Linux are used to set the system time, while the hwclock command is used to set and read and write the RTC time.
armsom@armsom:~$ sudo hwclock -r # View hardware time (RTC time)
2024-02-27 17:16:05.631917+08:00
armsom@armsom:~$ date # View system time
2024年 02月 27日 星期二 17:16:22 CST
armsom@armsom:~$ sudo date -s "2024-02-27 18:45:00" # Reset system time
2024年 02月 27日 星期二 18:45:00 CST
armsom@armsom:~$ sudo hwclock -w # Sync system time to RTC, time is not lost after power off